
Viz Artist User Guide
Version 3.14 | Published October 30, 2020 ©
Shadow Caster and Shadow Receiver
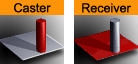
The Shadow Caster and Receiver plug-ins enable an object’s shadow to reflect on another object. To create a shadow item in a scene, two containers at a minimum must be used. The caster plug-in must be attached to one container and the receiver function to the other. The container acting as the caster must be positioned between the receiver container and a light source. For correct lighting calculation, a material is also required on the container. Objects that can function as a shadow receiver should be a built in 2D geometry or a font. An imported 2D geometry does not work.
Note: This plug-in is located in: Built Ins -> Container plug-ins -> Global
This page contains the following topics and procedures:
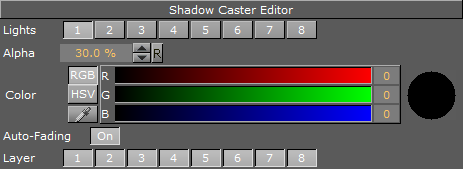
Shadow Caster Properties
-
Lights: Allows you to select which light sources are to shine on the caster object and thereby producing the shadow/shadows.
-
Alpha: Sets the alpha value and hence the transparency of the shadow being cast on the receiver objects.
-
Color: Allows you to define the shadows color.
-
Auto-Fading: With this option enabled, if you fade out a caster object either by using the alpha function or by adding a material with a low alpha value, the shadows created by the caster fades correspondingly. The option is enabled by default, since it looks right that the shadow fades out when the caster object fades out.
-
Layer: Allows you to select by which layer(s) the caster casts a shadow. You can select up to eight layers. Each layer corresponds to the layer selected in the Receiver objects. If you want all shadow casters to cast shadow on all receivers, you can set all layers on all casters and receivers to 1. If you want one caster to create shadow on some receivers and another caster to create shadow on different receivers, you select different layers for the sets of casters and corresponding receivers. Casters and receivers can have multiple layers enabled at the same time so you can set up a great number of combinations of caster/receiver combinations.
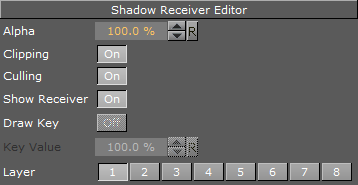
Shadow Receiver Properties
-
Alpha: Sets the alpha value.
-
Clipping: Cuts the shadow on the border of the object when set to On. When set to Off, the shadow is rendered onto the background outside the object, which normally looks wrong. Rendering with the clipping options set takes more resources than without. If you for instance have an infinite floor or a room with walls, you can switch of clipping without seeing the “false” shadows, and thereby save some rendering performance.
-
Culling: Decides in advance of the rendering process if the shadow is visible or if it is hidden by other objects. If that is the case, it skips it in the rendering process. If you know for sure that the shadow for an object in a scene should be rendered visible for the whole object, you can disable culling to save some rendering time, but the effect is marginal.
-
Show Receiver: Hides or shows the receiver object. If it is hidden, the shadow is still visible.
-
Draw Key: Adds key to the shadow. When enabled, the receiver must be hidden for the key to be drawn.
-
Key Value: Sets the key value.
Note: The Key Value setting is not available when Shadow Type in the Global Settings Panel is set to Shadow Map.
-
Layer: Allows you to select by which layers the receiver receives shadow. You can select up to eight layers. Each layer corresponds to the layer selected in the caster objects. If you want all shadow casters to cast shadow on all receivers, you can set all layers on all casters and receivers to 1. If you want one caster to create shadow on some receivers and another caster to create shadow on different receivers, you select different layers for the sets of casters and corresponding receivers. Casters and receivers can have multiple layers enabled at the same time so you can set up a great number of combinations of caster- and receiver combinations.
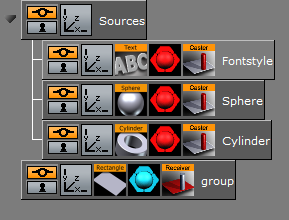
To Cast a Shadow
-
Add a group container to the Scene Tree
-
Name it Sources.
-
Add a Fontstyle and the Sphere and Cylinder Geometries as Sub-Containers of Sources.
-
Add a Material and the Shadow Caster plug-in to each Sub-Container.
-
Add a Group Container at the same level as the Sources Container
-
Add a Rectangle Geometry, a Material and the Receiver plug-in to it.

-
Position the Rectangle and the other objects such that the Sphere, Cylinder and text casts a shadow on the rectangular surface.
Caution: Containers are rendered twice when shadows are used.
Shadow Receiver Known Limitations
With shadows in Stencil Mode, the current implementation of the shadow receiver assumes that the receiving surface is flat and a standard geometry object, such as a rectangle, orientated on the XY plane. Non-flat geometries, and planes which are not extending in the XY plane, does not produce a properly casted shadow. However, by activating Shadow Map for the desired light source, shadows render correctly. Always make sure that the receiving object has a material.
See Also