
Viz Artist
Version 3.11 | Published August 27, 2018 ©
Ncam AR for Unreal Engine 4
The Viz Engine integration with NcamAR for Unreal Engine 4 (UE4) provides an interface between the Viz Engine and UE4. This integration lets you combine the photo realistic rendering capabilities of UE4 with the seamless functionality of template-based graphics provided by Vizrt. Here you find information on the technical aspects of installation and configuration, as well as instructions for end users:
Requirements
The following are the minimum requirements to use the Viz Engine integration with NcamAR for UE4:
System Requirements
-
HP Z4 G4 or HP Z8 G4
Hardware Requirements
-
Matrox X.mio3 or DSX LE4 video board.
-
Nvidia Quadro P6000.
Software Requirements
-
Windows 10 64-bit.
-
Viz Artist 64-bit Video version.
-
Epic Games Launcher (to install the Unreal Engine).
-
NcamAR for UE4.
Refer to the following version compatibility table for an overview of supported versions of the different software components:
|
Viz Artist |
Unreal Engine 4 |
NcamAR |
|
3.11.0 |
4.16.1, 4.16.2, 4.16.3 |
2.0.0 |
|
3.11.1 |
4.20.0, 4.20.1 |
3.0.0 |
Additional Licenses
-
NcamAR license
Installation
The NcamAR UE4 integration requires that Viz Artist and Engine is installed as platform type Video (see the Viz Engine Administrator Guide) . For instructions on how to install NcamAR for UE4 and Unreal Engine 4, refer to the NcamAR reference manual provided with the NcamAR installation package.
Configuration
These are the necessary configuration settings to activate the NcamAR UE4 integration in Viz Artist:
-
Configure the render options:
-
In Viz Configuration, select Render Options.
-
Activate the auxiliary rendering pipeline by setting Aux Rendering to Active.
-
Set Aux Camera to the camera number which is used to control the Camera Actor in UE4.
-
Set Render Scale to 1.2.
-
-
Activate the video input:
-
In Viz Configuration, select Video Input .
-
Activate a Live or Clip input and set it to the same video format as the configured output format of the Viz Engine.
-
-
Activate input Stream 1.
-
In Viz Configuration, select Video Input .
-
Activate input Stream 1 and set it to:
-
HD 720p if configured output format of the Viz Engine is set to 720p HD Progressive.
-
HD 1080pif configured output format of the Viz Engine is set to 1080i HD Interlaced or 1080p HD Progressive.
-
-
-
Configure input Stream 1 as Aux-Return channel.
-
In Viz Configuration, select Video Input: Stream Input.
-
Set Shared Memory > Unique Identifier to viz_aux_in_01.
-
Save the configuration changes and close Viz Artist.
-
Open the Viz configuration file and set stream_in_type to 3.
-
Use Cases
This section provides an overview of the supported use cases and their work flows. In addition, it outlines the scene set up and operation in Viz Artist.
Basic Workflow
The following provides a simplified overview of the software and hardware components, as well as the signal flows in a typical setup for the Viz Engine integration with NcamAR.
On a typical setup, both render engines, Viz Engine and UE4, run at the same time and on the same machine, which is connected to a camera tracking system through a Vizrt Tracking Hub. The image below illustrates the signal flow of the camera tracking data and video signal through the system.
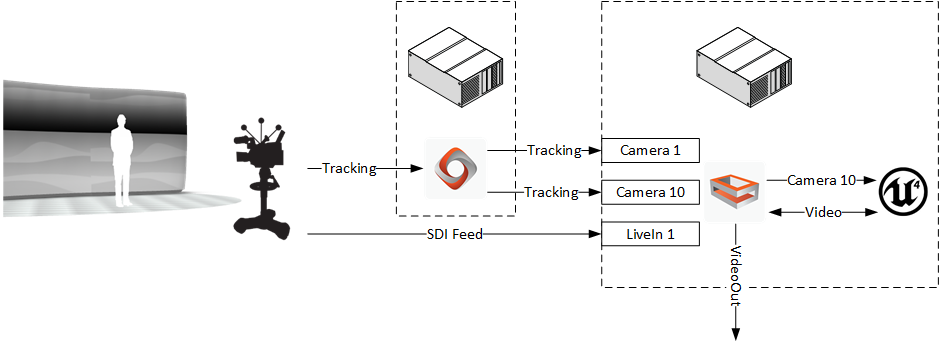
-
The Tracking Hub receives the tracking data of a camera from a tracking system. Usually, the incoming tracking data is mapped to two Viz Engine cameras inside the Tracking Hub, where one camera controls the rendering camera inside the Viz Engine (Viz-Camera) and the other the Camera Actor inside UE4 (Aux-Camera). This allows the user to adjust the delay between the two rendering engines using the Tracking Hub.
-
The Viz Engine receives a video signal from a camera over SDI as well as the tracking data of the Viz-Camera and Aux-Camera. The Viz Engine then applies the tracking data of the Viz-Camera to its internal rendering camera. Afterwards, the Viz Engine forwards the video signal and the tracking data of the Aux-Camera to the NcamAR I/O controller inside UE4.
-
The NcamAR I/O controller inside UE4 uses the supplied tracking data to render a matching viewpoint of the scene in UE4. Next, UE4 renders the UE4-Gfx layer and overlays it in the foreground (AR use case) or background (VS use case) of the video.
-
The N camAR I/O controller inside UE4 sends the composed video signal (Video + UE4-Gfx) back to the Viz Engine, where additional graphic layers can be rendered on top of the received signal.
-
The Viz Engine sends the final rendering result to its SDI output.
Augmented Reality (AR)
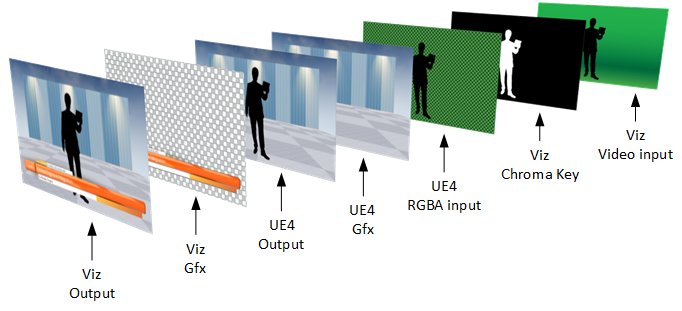
The AR use case adds an additional compositing layer to the scene that is loaded in the main layer of Viz Artist. This additional layer is referred to as the UE4-Gfx layer, and is overlaid onto the media asset that is set as scene background of the main layer scene in Viz Artist.
The image below illustrates the compositing steps and layers of the AR use case:
-
Viz Engine supplies a RGBA image of the video input with a full-screen key to the N camAR I/O controller .
-
UE4 renders and overlays the UE4-Gfx layer onto the video image.
-
Viz Engine renders additional graphics and overlays them onto the UE4 output.
Virtual Studio (VS)
The VS use case adds an additional compositing layer to the scene that is loaded in the main layer of Viz Artist. This additional layer is referred to as the UE4-Gfx layer, and is placed behind the media asset that is set as scene foreground of the main layer scene in Viz Artist.
The image below illustrates the compositing steps and layers of the VS use case:
-
Viz Engine generates the key/alpha channel for the video input by using its internal chroma keyer.
-
Viz Engine supplies a fill and key RGBA image of the video input to the N camAR I/O controller .
-
UE4 renders and overlays the UE4-Gfx (VS backdrop) layer behind the video image.
-
Viz Engine renders additional graphics and overlays them onto the UE4 output.
Scene Setup in Viz Artist
This section describes the scene setup in Viz Artist for Augmented Reality and Virtual Studio use cases.
AR Scene Setup
This section describes the scene setup in Viz Artist for the AR use case:
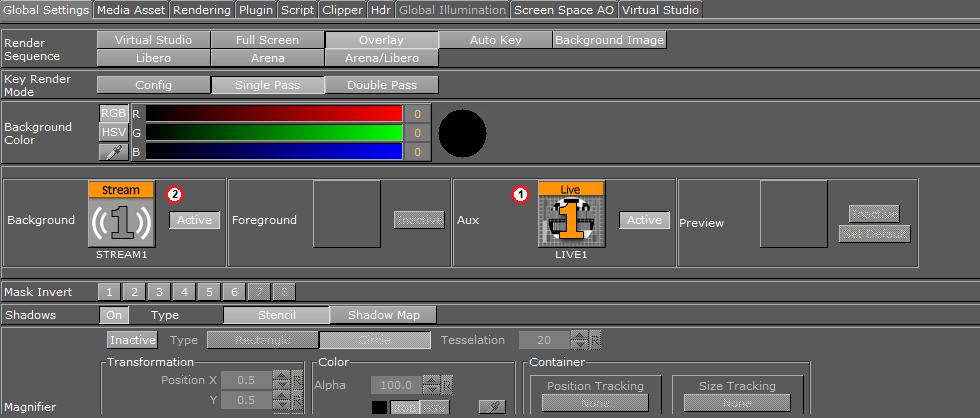
-
Set a video input as aux image (1).
-
Go to Built Ins > Media Assets .
-
Select the Live or Clip folder.
-
In the Properties pane, go to Scene Settings > Global Settings .
-
Select a Media Asset and drag it onto the Aux Image drop-zone.
-
-
Set stream input 1 as scene background (2).
-
Go to Built Ins > Media Assets .
-
Select the Stream folder.
-
Select a Media Asset Stream 1 and drag it onto the Background Image drop-zone.
-
VS Scene Setup
This section describes the scene setup in Viz Artist for the VS use case:
-
Set a video input as aux image.
-
Go to Built Ins > Media Assets .
-
Select the Live or Clip folder.
-
In the Properties pane, go to Scene Settings > Global Settings .
-
Select a Media Asset and drag it onto the Aux Image drop-zone.
-
-
Set stream input 1 as scene foreground.
-
Go to Built Ins > Media Assets .
-
Select the Stream folder.
-
Select a Media Asset Stream 1 and drag it onto the Foreground Image drop-zone.
-
-
Enable chroma keying of the video input:
-
Click on the Media Asset in the Media Asset Manager. This opens the Media Asset tab in the Scene Settings pane.
-
In the Keying Mode row, click the Chroma button.
-
Set the chroma keying configuration as described in Keying Mode Configuration.
-
Camera Control
This section contains information on how to setup the camera control in Viz Artist for setups that are connected to a camera tracking system, as well as information on how to use the NcamAR for UE4 integration without a camera tracking system.
Camera Controlled by a Camera Tracking System
Enable remote control of the Viz-Camera and Aux-Camera:
-
Click Views and select the Camera tab.
-
Set the Control mode of the Viz-Camera (Camera 1) and the Aux-Camera (Camera 10) to Remote.
-
Set Distortion Mode for both cameras to Internal.
-
Set Parameter Mode for both cameras to Lensfile.
-
Set the Viz-Camera (Camera 1) as active camera.
![]()
Camera Controlled by Viz Artist
Enable internal control of the Aux-Camera.
-
Click Views and select the Camera tab.
-
Set the Control mode of the Aux-Camera (Camera 10) to Editor.
-
Set Distortion Mode of the Aux-Camera (Camera 10) to Inactive.
-
Set the Aux-Camera (Camera 10) as active camera.