
Tracking Hub
Version 1.1.1 | Published April 03, 2018 ©
Configuration Panel
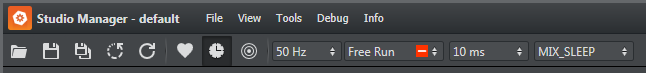
Use the Configuration Panel to save and load Studio configuration profiles, select modes of operation including frequency, and to set some user interface options.
-
Open: Open a Tracking Hub configuration file. The name of the currently loaded configuration file is always displayed in the top bar, between the application name and main menu.
-
Save: Save the current Studio configuration.
-
Save As: Save the current Studio configuration with a new name.
-
Reset: Reset the current Studio configuration. Note that the loaded configuration file is only changed if you click save after resetting the configuration.
-
Refresh: Reloads the actual configuration. Use this to apply any changes a third party software has made to the Tracking Hub parameters, so that the changes can visualized in the Studio Manager.
-
View Log: Open or close the Log Panel.
-
View Timing Analysis: Open the Timing Analysis Window.
-
Frequency: Select the production frequency; 50 Hz, 60 Hz or 59.94 Hz.
-
Synchronization Mode: Select synchronization mode for the Tracking Hub:
-
Freerun: No synchronization. The Tracking Hub uses its own time base, corresponding with the configured frequency.
-
AV-Card: Synchronization is done by an installed Plura card.
-
Viz Engine: Synchronized with Viz Engine, running on the same computer.
Tip: If the selected synchronization mode is followed by a red box with a white horizontal line, this indicates synchronization issues.
-
-
Send Delay: The time Tracking Hub waits until it sends tracking data to the engine. This setting is especially important if your tracking delay is less than 1 field.
With the help of the Timing Analysis, the transmission time can be set after the arrival of the tracking data. If your tracking delay is larger than 1 field, set the send delay value to No Delay. This reduces the CPU usage. -
Busy Loop: If it is necessary to set the Send Delay, use Busy Loop to select the way this happens. This setting depends mainly on your hardware.
-
WITH SLEEP: Lowest CPU load, less exact.
-
MIX SLEEP: Uses both WITH and NO SLEEP, almost exact.
-
NO SLEEP: Highest CPU load, exact.
-
See Also