This section provides detailed network and firewall information for achieving optimal configuration and performance in Tricaster Now.
Firewall Ports
Tricaster Now mandates that the computer operating both Launchpad and NDI Bridge (Join) must have access to specific network ports.
It is essential to ensure these ports are open and available for seamless functionality.
Source | Destination | Protocol | Port | Service | Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
<client network> For example: 192.168.0.0/24 | <Tricaster Now Instance's Public IP> | TCP | 443 | Live Panel | Secure access to Tricaster Now cloud switcher through web browser. |
TCP | 8443 | Remote Access (Nice DCV) | Secure Remote Access facilitates a connection from an on-premises location to your Tricaster Now instance. By default, this secure remote access utilizes either TCP 8443 or UDP 8443 ports. The system intelligently checks the availability of UDP 8443 first. If not accessible, it automatically switches to using TCP 8443, ensuring a seamless and flexible connectivity experience. IMPORTANTFor optimal performance in environments with high latency and fluctuating bandwidth, such as 5G networks and broadband connections, it is crucial to confirm that the UDP 8443 port is accessible. This ensures a more stable and efficient connection under these variable network conditions. | ||
UDP | 8443 | ||||
TCP | 5990 | NDI Bridge | NDI Bridge ports IMPORTANTTo maximize performance, given the unique characteristics of the NDI protocol, it is essential to properly configure UDP protocol ports. This setup is key to leveraging the full potential of the NDI protocol's capabilities. | ||
UDP | 5990 | ||||
TCP | 9001-9020 | SRT feeds | SRT Ports These ports are used to send an SRT signal from on premises / remote location to the Tricaster Now's cloud switcher. IMPORTANTThe UDP protocol is vital for SRT (Secure Reliable Transport) signals as it offers low-latency transmission, crucial for real-time streaming. It enhances reliability in packet delivery, ensuring high-quality video and audio streaming. | ||
UDP | 9001-9020 | ||||
TCP | 49152 - 65535 | Ephemeral Ports for SRT and NDI Bridge | Temporary additional ports used by NDI Bridge and SRT feeds. Ephemeral ports play a critical role in NDI Bridge and SRT feeds by providing dynamic, temporary communication endpoints for streaming video and audio data. These ports facilitate seamless, on-demand connections between devices, enhancing flexibility and scalability in cloud live production environments. | ||
UDP | 49152 - 65535 |
NDI Ports
When planning your production, it is important to review firewall ports mentioned on on-premises and remote installations LAN that will be transmitting NDI feeds to Tricaster Now. Sometimes an NDI transmission issue can arise due a limitation in the network of the remote side and not in the cloud.
Port number | Type | Use |
|---|---|---|
5353 | UDP | Port used for mDNS communication |
5959 | TCP | NDI Discovery Server. Optional and beneficial in large configurations, when you need to connect NDI devices between subnets or if mDNS is blocked. |
5960 | TCP | This is a TCP port used for remote sources to query a machine and discover all of the sources running on it. This is used for instance when a machine is added by an IP address in the access manager so that from an IP address alone all of the sources currently running on that machine can be discovered automatically. |
5961 and up | TCP | These are the base TCP connections used for each NDI stream. For each current connection (at least one port number is used in this range). Common implementations: 5961 ~ 7000 |
5990 | TCP/UDP | Port used by NDI Bridge |
5960 and up | UDP | In version 5 and above, when using reliable UDP connections it uses a very small number of ports in the range of 5960 for UDP. These port numbers are shared with the TCP connections. Because connection sharing is used in this mode, the number of ports required is very limited and only one port is needed per NDI process running and not one port per NDI connection. |
6960 and up | TCP/UDP | When using multi-TCP or UDP receiving, at least one port number in this range is used for each connection. |
7960 and up | TCP/UDP | When using multi-TCP, unicast UDP, or multicast UDP sending, at least one port number in this range is used for each connection. |
Network Design Best Practices
This section offers expert insights and guidelines for designing a network tailored for hosting live productions, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Configuring NDI Protocols and Receive Mode
NDI Protocols employ advanced methods for transmitting video and audio over networks:
Reliable UDP: A new addition, excels in challenging network setups, featuring superior congestion control, loss recovery, bandwidth management, and high latency support, ideal for WAN or Wi-Fi.
Multipath TCP: Enhances network utilization by leveraging multiple network paths and NICs, optimizing throughput and redundancy across various networks, including wireless and mobile.
UDP with Forward Error Correction: Suitable for applications where timely delivery trumps accuracy, like streaming media or VoIP, using duplicated data for error control.
Single TCP: Ensures reliable data packet exchange and delivery between host systems.
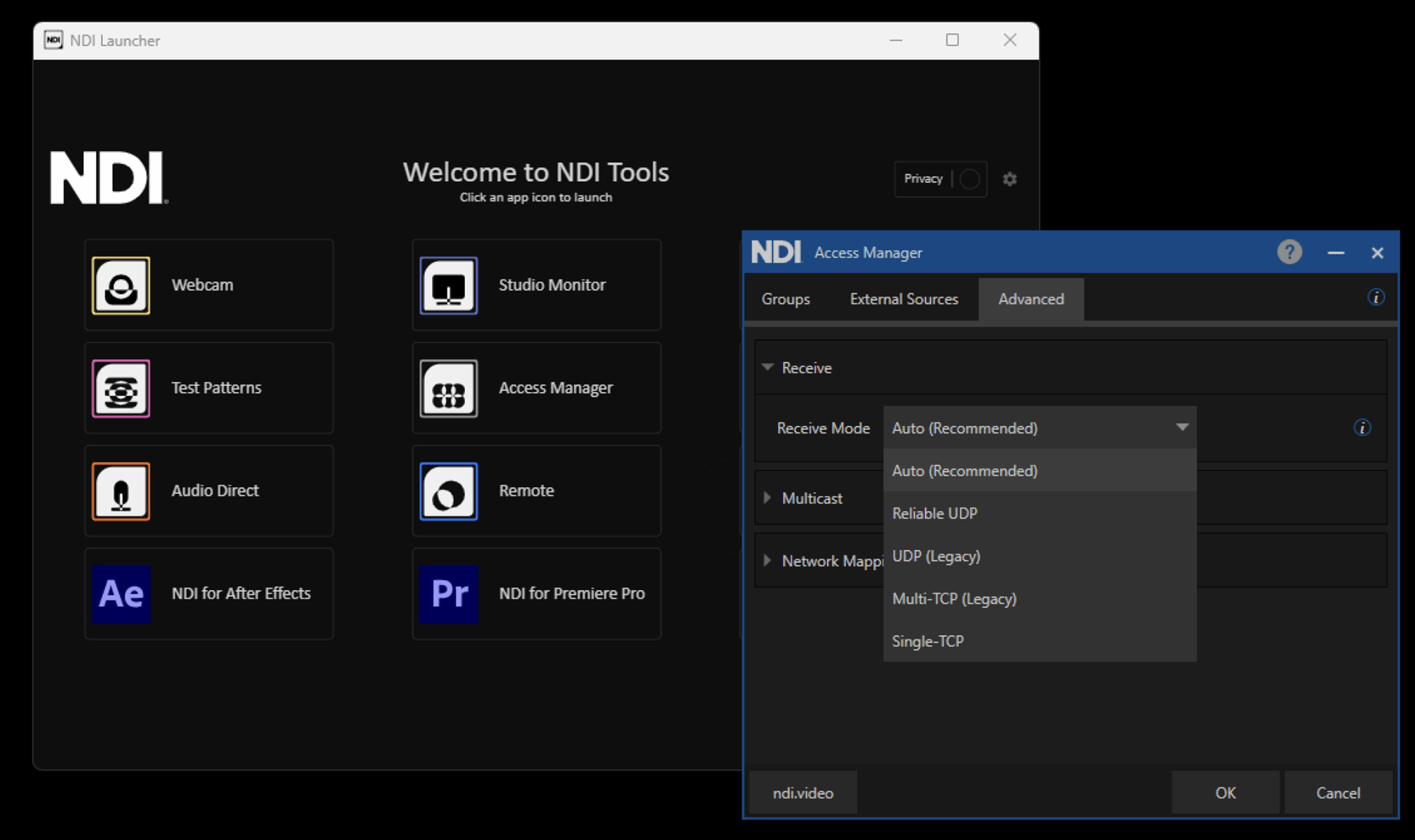
To Configure Received Mode
Configure Received Mode in the NDI Access Manager for all devices involved in the cloud live production.
IMPORTANT
Note: For seamless utilization of NDI Protocols, it is recommended to keep the configuration setting at Auto if you are not sure.
This default mode enables the NDI Protocol to automatically select the most suitable protocol based on the prevailing network conditions, such as port availability and switch configurations, ensuring optimal performance without manual intervention.
Infrastructure
This section provides guidelines for designing and maintaining a network optimized for your live production.
Cables
Verify RJ-45 connectors termination quality to avoid issues related to bad performance or errors.
Ethernet cable should be made of copper, avoid aluminum with copper coating.
Switches
When selecting a network switch, prefer to use a managed layer 2 switch at minimum.
Prioritize throughput speeds. Ensure all ports support full duplex communication with at least 1 Gigabit per second (Gbps) upstream and downstream data speeds.
For managed switches, manually set ports to 1 Gbps to avoid potential Auto Negotiation issues resulting in slower connections.
Consider switches with 10 Gbps, but be cautious about shared bandwidth across multiple ports in the backplane, especially for inter-switch connections.
To minimize security concerns and non desired traffic interference, isolate NDI traffic from important corporate data using VLANs.
Disable QoS (NDI does not use), if you have other software that is QoS enabled (like Dante), then using VLAN to separate networks like mentioned above.
Enable Flow Control, for preventing an interface from overloading a destination, which in turn would cause dropped packets.
IGMP Snooping: For NDI Multicast.
Activate this feature only if you have comprehensive expertise in networking.
Needs can vary and specific features might be required at times. This chart is breaks down switch selection into three categories: Small, Medium and Large.
Small | Medium | Large | |
Number of NDI Channels | 8 channels or less | 9 to 60-100 channels | Over 60-100 channels |
Interface Types | All 1GbE | Mostly 1GbE Some 10GbE | 1GbE and 10GbE |
Video Formats | HD | HD/UHD/4K | HD/UHD/4K |
Switch Recommendations | Any unmanaged or managed switch | Managed Layer 2 switch | Cut-Through switch |
Network Monitoring
Deploy monitoring software to track NDI traffic and devise a comprehensive strategy for identifying, executing, and conducting detailed monitoring of:
NDI Devices
Network bandwidth usage.
Network anomalies.
NDI Sources and Feeds
Video resolution and frame rate.
Frame format.
Audio channel count.
Audio frame rate.
Security Recommendations
Important tasks to enhance the security of your NDI Network.
Firewall Rules
To lessen the attack surface, configure firewall rules to restrict NDI traffic to only NDI devices, ports, and protocols.
Regular Operating System and NDI Software Updates
To address any vulnerabilities:
Keep operating system up to date with the most recent security patches.
Keep hardware up to date with the most recent patches and firmware.
Keep network switch firmware and software up to date with the latest security patches and bug fixes to address known vulnerabilities.
Always work with the latest version of NDI-enabled software.