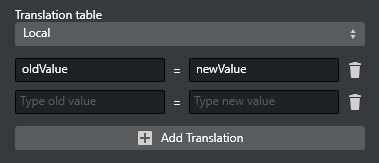
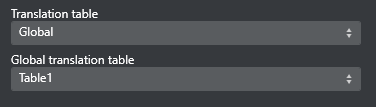
Translation tables can be used to define arbitrary value-translations, via an oldValue=newValue table. There are two kinds of translation tables:
Local: settings configured locally per page field.
Global: the Global Translation Table can be configured in Channel Settings under Page Content Filling > Translation Tables.
Match and replace rules in translation table: There are some special characters can be used in the old value (left part) of the translation table that have special rules when trying to match and replace the value. It also supports partial match, * means one or more characters, ? means one character.
Symbol(s) | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
* | Match and replace - wildcard pattern |
|
? | Match and replace - wildcard a specific number of characters |
|
() | Match and replace a substring |
|
[] | Match and replace the character. |
|