The DataReader plug-in allows for reading feeds of information from several different types of sources of information.
DataReader supports reading Excel files, databases using SQL, feeds using XML and JSON. The plug-in also supports different types of outputs.
Note: This plug-in is located in: Plugins -> Container plug-ins -> Data
Information: DataPool plug-ins only work properly on a single channel on the same machine.
The plug-in shows different arguments depending on the inputs and the outputs used:
Functionality
All of the different sources of information behave the same way: They all search for records and translate the records fields to a certain format according to the requested output type. In the case of DataPool output types, the plug-in converts each incoming record to a DataPool command and executes it. In the case of Shared Memory, the plug-in creates a character separated string of fields and pushes to shared memory.
Important! To read from Microsoft Excel files, Microsoft Access Database Engine is necessary. If the Microsoft Office installer did not install Microsoft Access Database Engine, it needs to be installed with the same software architecture (x64 or x86) as Microsoft Office.
Input Type - Excel
In this mode the plug-in reads a sheet from an Excel file. The parameters in this mode are:
File Name: Determines the name of the file to be read.
Table/Sheet: Determines the name of the sheet to be read from within the file.
Key: Determines the name of the column in the Excel file from which the keys to the DataTable should be taken.
From row: Determines the row number in the Excel sheet from where to start reading the records.
Number of rows: Determines the maximum number of records to read, starting from the row stated in From row.
Fields to Read: Specifies by name the columns to read.
DP Field Name: Specifies the field name in DataPool where to write the output.
Field is a: Specifies the type of the target. In case of Shared Memory, the following parameters are changed:
DP Field Name: Hidden.
Shared Memory Variable: The variable for Shared Memory to be used.
Fields Delimiter: The delimiter to use for different fields.
Rows Delimiter: The delimiter to use for different rows.
Post Update Action: Specifies commands (either DataPool or Viz commands) to be executed right after the data is read and sent to the target.
Show Data: Dumps the data the plug-in reads to a DataPool variable called
READER_CONSOLEwhen set toOn. This is extremely useful for development and debugging purposes. This dump includes error messages too.Return Variables Prefix: Specifies a prefix to add to the name of the DataPool variables that the plug-in uses. For example, if the prefix is
STV_, then the plug-in dumps the debug information toSTV_READER_CONSOLE.Load Automatically: Reads the information automatically every certain amount of time. This amount of time is defined in Automatic Load Period (in seconds).
Automatic Load Period (in seconds): Specifies the period of time between consecutive automatic reads.
Load: Invokes the action of reading the data.
Example
Preparation
Debug Information
For these examples, we want to see if any errors occur or if the data is correct. To prepare this debug mode, create a container with a Font and a DataText plug-in. Set the Field Name of the DataText plug-in to READER_CONSOLE.
Data Source
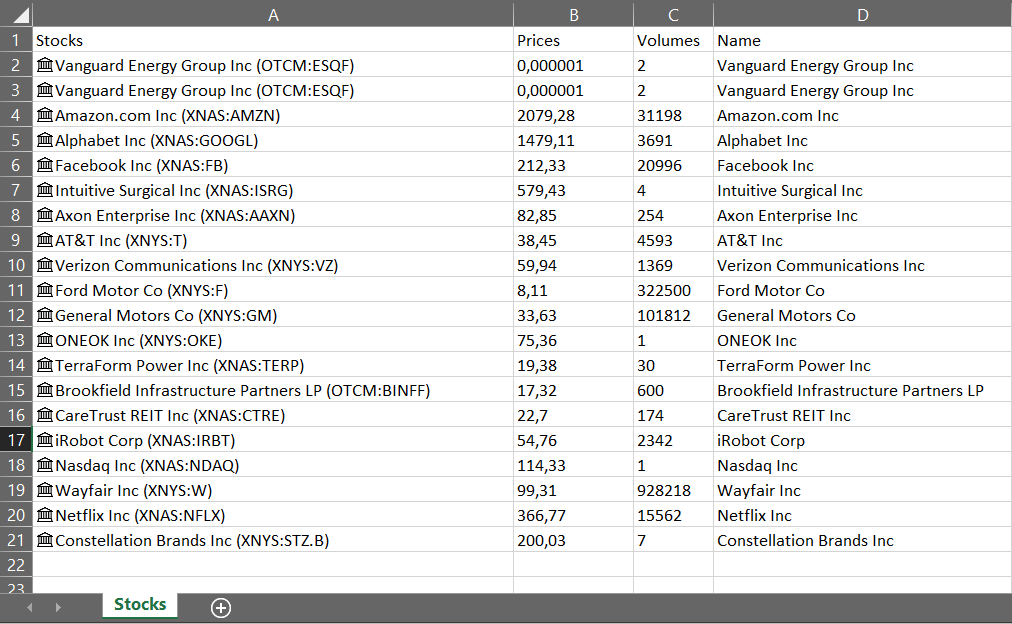
The following is a typical example of a table in an Excel sheet we would be interested in reading from using DataReader. Create a similar file (the headings have to match) and save it under C:\temp\Indexes.xlsx.
DataPool Type
A matching DataPool type is needed for this example. Create a file %PROGRAMDATA%\Vizrt\VizEngine\DataPool\Stocks.dp with following content:
Stocks.dp
Stocks = { string Prices; string Volumes; string Name;};Setup
DataReader
Create a container with a DataReader plug-in on it. In this case, configure the DataReader plug-in as following:
Query type = EXCEL
File name = C:\temp\Indexes.xlsx
Table/Sheet = Stocks
Key = Name
From Row = 5
Number of Rows = 4
Fields To Read = Prices,Volumes,Name
DP Field Name = Indexes
Show Data = On
DataArray
Set the DataReader parameter Field is a: to DataArray.
Create a new container with a DataArray plug-in and set following configuration:
Field Name = Indexes[4]
Type = Stocks
Now click the Load button in the DataReader plug-in to load the data into the DataArray. You should see the results on the DataText container:
READER_CONSOLE
Indexes[0]={ { Prices=""579,43""; Volumes=""4""; Name=""Intuitive Surgical Inc""; };};Indexes[1]={ { Prices=""82,85""; Volumes=""254""; Name=""Axon Enterprise Inc""; };};Indexes[2]={ { Prices=""38,45""; Volumes=""4593""; Name=""AT&T Inc""; };};Indexes[3]={ { Prices=""59,94""; Volumes=""1369""; Name=""Verizon Communications Inc""; };};READER_NUM_RECORDS=9;
Click the Dump button on the scene plug-in DataPool and the console prints your DataPool data:
DataPool Dump
Indexes[0-3]={ { Name=Intuitive Surgical Inc; Prices=579,43; Volumes=4; }, { Name=Axon Enterprise Inc; Prices=82,85; Volumes=254; }, { Name=AT&T Inc; Prices=38,45; Volumes=4593; }, { Name=Verizon Communications Inc; Prices=59,94; Volumes=1369; }};DataTable
Set the DataReader parameter Field is a: to DataTable. Create a new container with a DataTable plug-in and set following configuration:
Field Name = Indexes
Type = Stocks
Now click the Load button in the DataReader plug-in to load the data into the DataArray. You should see the results on the DataText container:
READER_CONSOLE
Indexes[Intuitive Surgical Inc]={ { Prices=""579,43""; Volumes=""4""; Name=""Intuitive Surgical Inc""; };};Indexes[Axon Enterprise Inc]={ { Prices=""82,85""; Volumes=""254""; Name=""Axon Enterprise Inc""; };};Indexes[AT&T Inc]={ { Prices=""38,45""; Volumes=""4593""; Name=""AT&T Inc""; };};Indexes[Verizon Communications Inc]={ { Prices=""59,94""; Volumes=""1369""; Name=""Verizon Communications Inc""; };};Click the Dump button on the scene plug-in DataPool and the console prints your DataPool data (note that the Key parameter in the DataReader plug-in is used to obtain the column from the indexes of the table):
DataPool Dump
Indexes[Axon Enterprise Inc,Intuitive Surgical Inc,AT&T Inc,Verizon Communications Inc]={ { Name=Axon Enterprise Inc; Prices=82,85; Volumes=254; }, { Name=Intuitive Surgical Inc; Prices=579,43; Volumes=4; }, { Name=AT&T Inc; Prices=38,45; Volumes=4593; }, { Name=Verizon Communications Inc; Prices=59,94; Volumes=1369; }};DataStructure
Set the DataReader parameter Field is a: to DataStructure and remove the DP Field Name. Create a new container with a DataStructure plug-in and set following configuration:
Field Name = Axon Enterprise Inc
Create three containers under the DataStructure container level and add a font and DataText to every of them. Set the Field Names of the three DataTexts to Prices, Volumes and Name. Now click the Load button in the DataReader plug-in to load the data into the DataArray. You should see the results on the DataText container:
READER_CONSOLE
Intuitive Surgical Inc={ Prices=""579,43""; Volumes=""4""; Name=""Intuitive Surgical Inc"";};Axon Enterprise Inc={ Prices=""82,85""; Volumes=""254""; Name=""Axon Enterprise Inc"";};AT&T Inc={ Prices=""38,45""; Volumes=""4593""; Name=""AT&T Inc"";};Verizon Communications Inc={ Prices=""59,94""; Volumes=""1369""; Name=""Verizon Communications Inc"";};Click the Dump button on the scene plug-in DataPool and the console prints your DataPool data (note that the Key parameter in the DataReader plug-in is used to obtain the column from the indexes of the table):
DataPool Dump
Axon Enterprise Inc ={ Name=Axon Enterprise Inc; Prices=82,85; Volumes=254;}DataFieldArray
Set the DataReader parameter Field is a: to Data Field Array. Create a new container with a DataText plug-in and set following configuration:
Field Name = Indexes[2-3]
This fetches a sub array from the Indexes Data Field Array starting with index 2 (3rd element).
Create a containers under the DataText container level and add a font to it.
Info: We could use multiple sub containers to show multiple values of the created sub array (Indexes[2-3]). This array has two values, so we could create two font containers below the DataText container to display them.
Now click the Load button in the DataReader plug-in to load the data into the Data Field Array and display the third value in the DataText's sub container. You should see the results on the DataText container:
READER_CONSOLE
DFA[0-8]=""Axon Enterprise Inc"",""AT&T Inc"",""Verizon Communications Inc"",""Ford Motor Co"";READER_NUM_RECORDS=9;
Click the Dump button on the scene plug-in DataPool and the console prints your DataPool data (note that the Key parameter in the DataReader plug-in is used to specify the column from the values):
DataPool Dump
DFA[0-2]=Axon Enterprise Inc,AT&T Inc,Verizon Communications Inc
Shared Memory
Set the DataReader parameters:
Field is a: = Shared Memory
Shared Memory Variable = Indexes
Create a new container with a DataText plug-in, a SHMTracker plug-in and a font and set following configuration:
DataText plug-in:
Field Name = Output
SHMTracker plug-in:
Output Field Name = Output
Shared Memory Key Name = Indexes
Now click the Load button in the DataReader plug-in to load the data into the Shared Memory. You should see the results on the debug DataText container and the Output DataText container:
READER_CONSOLE
579,43|4|Intuitive Surgical Inc|82,85|254|Axon Enterprise Inc|38,45|4593|AT&T Inc|59,94|1369|Verizon Communications Inc|
Input Type - SQL
In this mode, the plug-in reads a sheet from a database that supports SQL. The parameters in this mode are:
Connection String: Connects to the database using the connection string. Each type of database has a different connection string. A good reference on connection strings for several different databases can be found in http://www.connectionstrings.com/.
SQL Query: Queries the database using SQL command.
Key: Determines the name of the column in the read query or table from which the keys to the DataTable should be taken.
From row: Determines the row number in the query/table from where to start reading the records.
Number of rows: Determines the maximum number of records to read, starting from the row stated in From row.
Fields to Read: Specifies by name the columns to read.
DP Field Name: Specifies the field name in DataPool where to write the output.
Field is a: Specifies the type of the target. In case of Shared Memory following parameters are changed:
DP Field Name: Hidden.
Shared Memory Variable: The variable for Shared Memory to be used.
Fields Delimiter: The delimiter to use for different fields.
Rows Delimiter: The delimiter to use for different rows.
Post Update Action: Specifies commands (either DataPool or Viz commands) to be executed right after the data is read and sent to the target.
Show Data: Dumps the data the plug-in reads to a DataPool variable called
READER_CONSOLEwhen set toOn. This is extremely useful for development and debugging purposes. This dump includes error messages too.Return Variables Prefix: Specifies a prefix to add to the name of the DataPool variables that the plug-in uses. For example, if the prefix is
STV_, then the plug-in dumps the debug information toSTV_READER_CONSOLE.Load Automatically: Reads the information automatically every certain amount of time. This amount of time is defined in Automatic Load Period (in seconds).
Automatic Load Period (in seconds): Specifies the period of time between consecutive automatic reads.
Load: Invokes the action of reading the data. The different types of outputs are exactly as in the case of Excel.
Input Type - XML
This mode allows for reading XML feeds. These can be read from a remote server or from a local file.
These can be read from a remote server or from a local file.
The parameters in this mode are:
File Name: Shows the full name of a file or a URI to a remote file to be read.
Use Authentication: Allows entering a user name and password In the case the File Name is a URI and the remote server requires Basic Authentication.
Avoid Cache: Avoids using cache mechanisms that avoid the refresh of data changing in the server side in the case of a remote file. This is useful when reading information that changes. The caching mechanism avoids the plug-in to get the updates. When “Avoid Cache” is on the plug-in gets the freshest information.
XPath: States what records to search for. For an explanation of the XPath syntax please refer to http://www.w3.org/TR/xpath/. For examples of how to use XPath please refer to https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms256086.
Namespaces: Specifies namespaces for use in XPath expressions when it is necessary to define new namespaces externally. Namespaces are defined in the XML style, as a space-separated list of namespace declaration attributes. You can use this property to set the default namespace as well. An example of the definition of namespaces could be:
xmlns:na='http://myserver.com' xmlns:nb='http://yourserver.com'Key: Determines the name of the field in the read records from which the keys to the DataTable should be taken.
From row: Determines he row number in the read record from where to start reading the records.
Number of rows: Determines the maximum number of records to read, starting from the row stated in From row.
Fields to Read: Specifies by name the fields to read from the records.
DP Field Name: Specifies the field name in DataPool where to write the output.
Field is a: Specifies the type of the target. In case of Shared Memory following parameters are changed:
DP Field Name: Hidden.
Shared Memory Variable: The variable for Shared Memory to be used.
Fields Delimiter: The delimiter to use for different fields.
Rows Delimiter: The delimiter to use for different rows.
Post Update Action: Specifies commands (either DataPool or Viz commands) to be executed right after the data is read and sent to the target.
Input Format: Specifies the format of the XML file.
Output Format: Specifies the format for the DataPool output.
Show Data: Dumps the data the plug-in reads to a DataPool variable called READER_CONSOLE when set to
ON. This is extremely useful for development and debugging purposes. This includes error messages too.Return Variables Prefix: Specifies a prefix to add to the name of the DataPool variables that the plug-in uses. For example, if the prefix is
STV_, then the plug-in dumps the debug information toSTV_READER_CONSOLE.Load Automatically: Reads the information automatically every certain amount of time. This amount of time is defined in Automatic Load Period (in seconds).
Automatic Load Period (in seconds): Specifies the period of time between consecutive automatic reads.
Load: Invokes the action of reading the data.
Use Custom Headers: Adds custom HTTP headers to the request. For example, this can be used to specify an API token for web services.
Input Type - JSON
This mode allows for reading JSON feeds. These can be read from a remote server or from a local file.
The parameters in this mode are:
File Name: Shows the full name of a file or a URI to a remote file to be read.
XPath: States what records to search for. This is a subset of the standard XPath.
Key: Determines the name of the field in the read records from which the keys to the DataTable should be taken.
From row: Determines the row number in the read record from where to start reading the records.
Number of rows: Determines the maximum number of records to read, starting from the row stated in From row.
Fields to Read: Specifies by name the fields to read from the records.
DP Field Name: Specifies the field name in DataPool where to write the output.
Field is a: Specifies the type of the target. In case of Shared Memory following parameters are changed:
DP Field Name: Hidden.
Shared Memory Variable: The variable for Shared Memory to be used.
Fields Delimiter: The delimiter to use for different fields.
Rows Delimiter: The delimiter to use for different rows.
Post Update Action: Specifies commands (either DataPool or Viz commands) to be executed right after the data is read and sent to the target.
Show Data: Dumps the data the plug-in reads to a DataPool variable called
READER_CONSOLEwhen set toOn. This is extremely useful for development and debugging purposes. This dump includes error messages too.Return Variables Prefix: Specifies a prefix to add to the name of the DataPool variables that the plug-in uses. For example, if the prefix is
STV_, then the plug-in dumps the debug information toSTV_READER_CONSOLE.Load Automatically: Reads the information automatically every certain amount of time. This amount of time is defined in Automatic Load Period (in seconds).
Automatic Load Period (in seconds): Specifies the period of time between consecutive automatic reads.
Load: Invokes the action of reading the data.
Proxy on/off
Proxy Mode:
Auto Detect: Detects if there is a proxy set in the system or Engine.
System Settings: Sets the proxy for HTTP requests to the system proxy.
Manual Configuration: Configures a proxy manually with a Proxy URL, Proxy User Name and Proxy Password.
Use Custom Headers: Adds custom HTTP headers to the request. This can for example be used to specify an API token for web services.