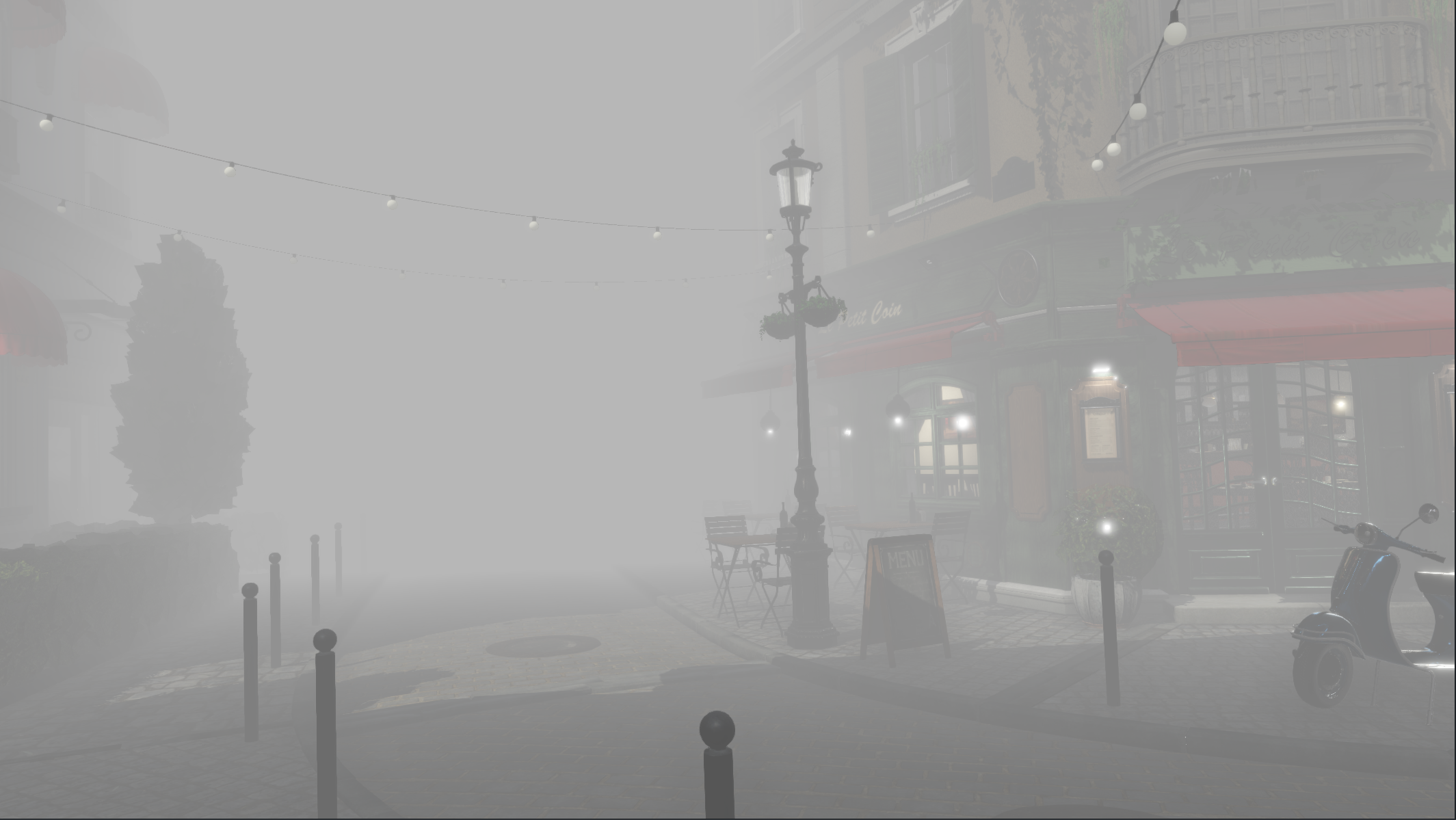
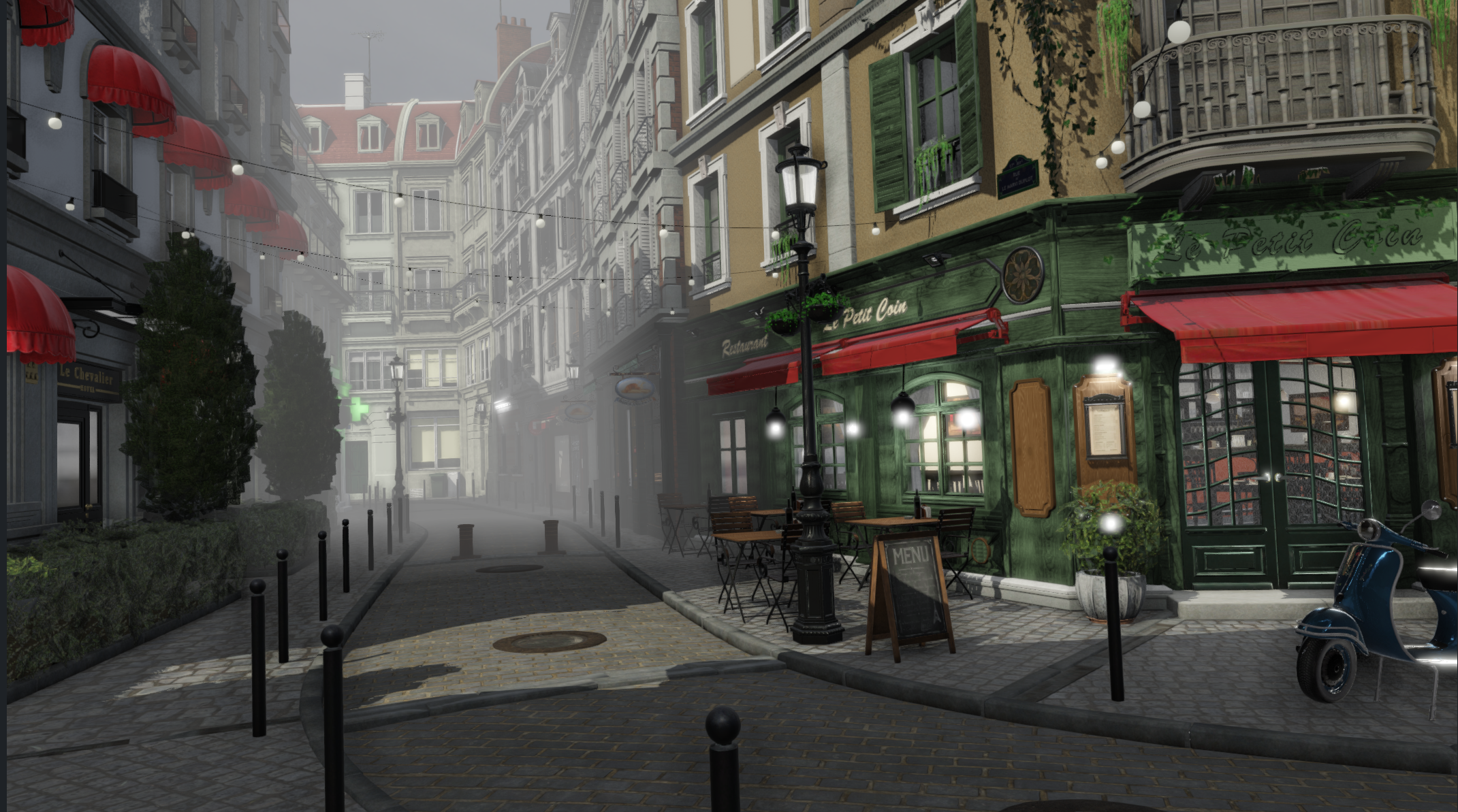
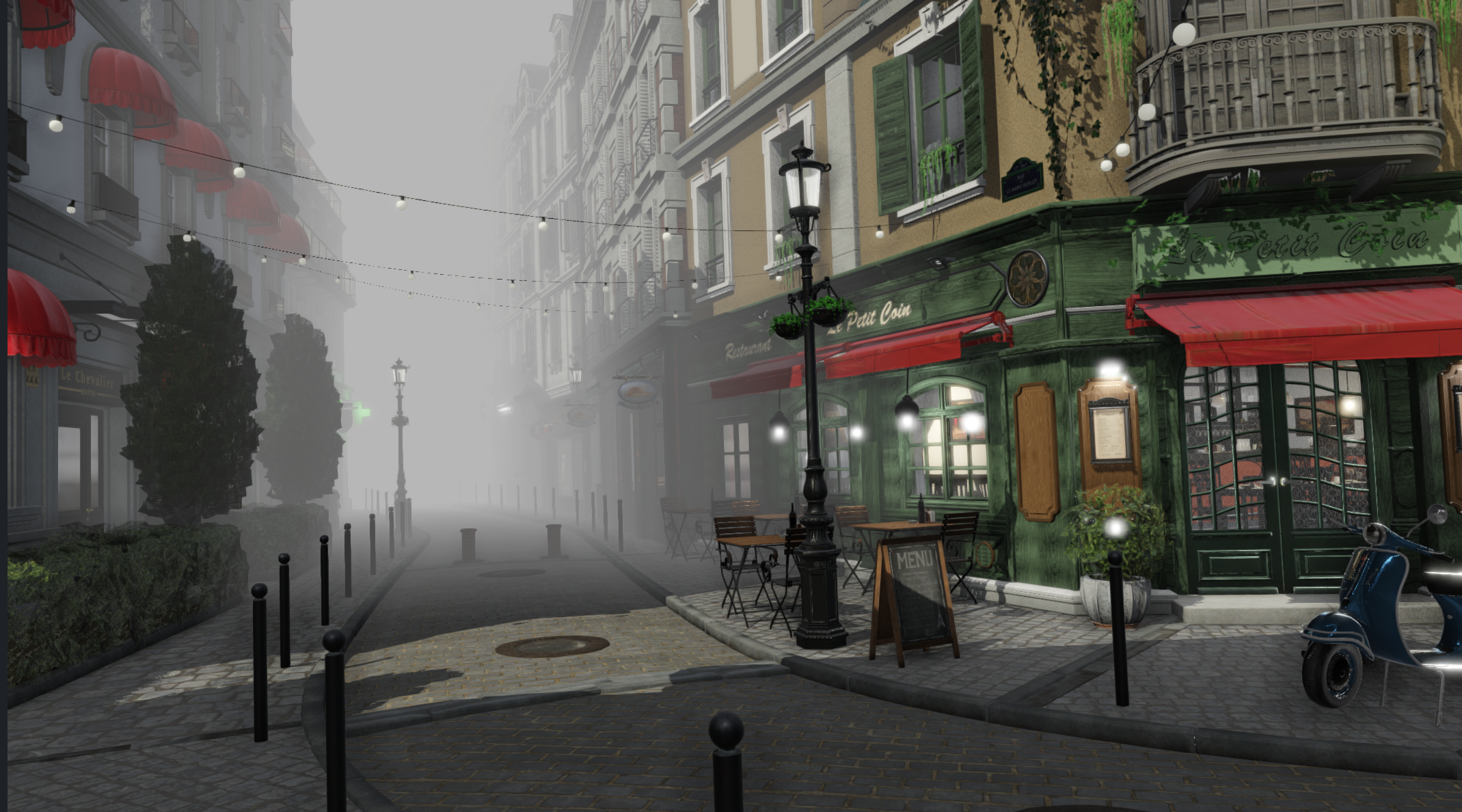
A Fog adds depth to the scene. It represents dust and dirt in the air at a given distance. The Fog effect is located in Scene Settings-Rendering inside the Post Processing effects.
Fog Parameters
Effect
Fog Mode: Sets how the transmittance through the fog is calculated.
Composition Mode: Sets how the effect is composed to the main scene color. The following options are available:
Linear Interpolation: Composes by performing linear interpolation between scene the scene color and the fog color.
Multiply: Composes by dimming the scene according to how dense the fog is, with respect to the fog color. It is recommended to use this mode while having volume-casting lights in the scene.
Intensity: Sets the intensity of the effect applied to the scene.
Start: Sets the distance where the fog starts from the camera.
Length: Sets the length of the fog from the camera. Only available for Linear Fog Mode.
Density: Sets the fog particles density.
Scattering: Sets how much light is scattered on fog particles. This is the antecedent of the scattering-to-absorption ratio.
Absorption: Sets how much light is absorbed by fog particles. This is the consequent of the scattering-to-absorption ratio.
Phase: Sets how the light is scattered on fog particles. The negative value means the light is likely to be reflected, while the positive value means the light is likely to be transmitted.
Color: Sets the color of the fog particles.
Ray Marching
Half Resolution: Sets whether ray marching is performed in half resolution. This speeds up the computation at the cost of the quality.
Profile: Sets what ray marching prioritizes. The options are Performance, Balanced, and Quality.
Bias: Sets the bias of ray marching.
0means to evenly sample along the ray, while1means to mostly sample near the camera. This could also reduce noise when the farthest point in the scene is deterministic.
Temporal Reprojection
Frames: Determines the number of frames used to accumulate the effect (higher values can cause ghosting for moving objects/camera).
Reprojection Strength: Controls how strong the rays are reprojected for moving objects.
Denoising
Blur Kernel: Controls the quality of denoising.
Blur Iterations: Controls how strong the effect gets denoised.
Light Volumes
The fog also acts as a participating media for lights by nature, and it leads to a light volume with respect to the light type. This process of simulation requires ray marching and denoising controlled by the parameters in Ray Marching, Temporal Reprojection, and Denoising groups. To setup volume casting behavior of a particular light when the fog is enabled, see Light and Shadows.
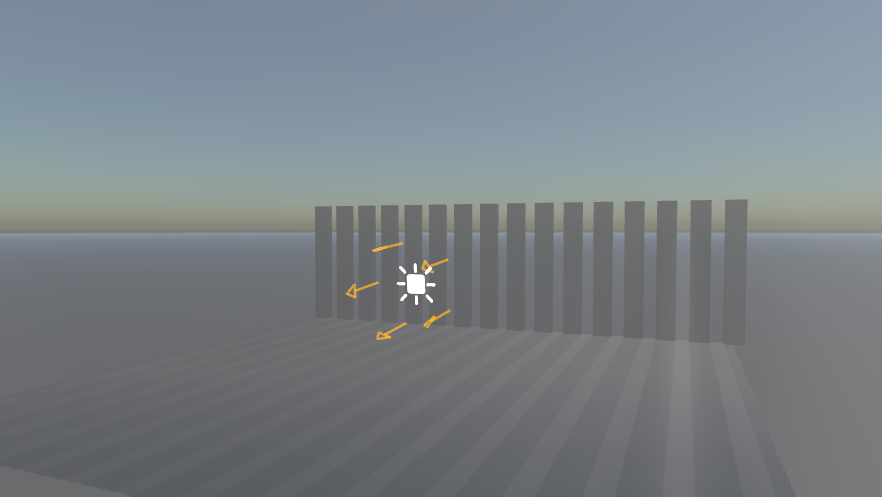
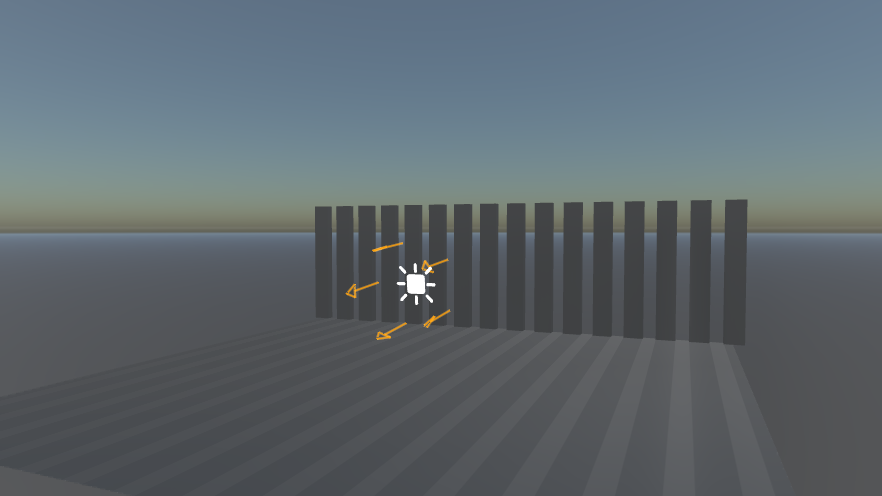
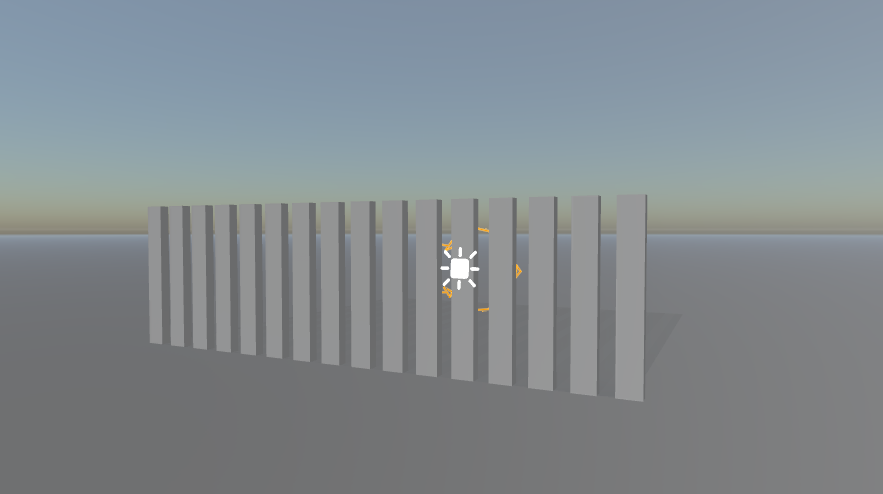
Examples
Screenshot | Fog Settings |
|---|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
(Notice the light direction) | |
(Notice the light direction) | |
(Notice the light direction) | |
(Notice the light direction) |